UMG ViewModels
Introduction
The ViewModel layer is the bridge between backend interaction data and your UMG widgets.
In the Interaction System, ViewModels observe the live interaction state and expose it as UI-friendly fields so prompts and HUD elements can update reactively without hard-wiring gameplay logic into widgets.
Backend Data
The backend exposes the current Interaction State, which ViewModels present from two complementary information perspectives:
Interaction Source: Represents the instigator (player or AI) and its relationship to nearby targets.
Interaction Target: Represents data from the target, and the current state of its possible interactions.
Actor Prompts
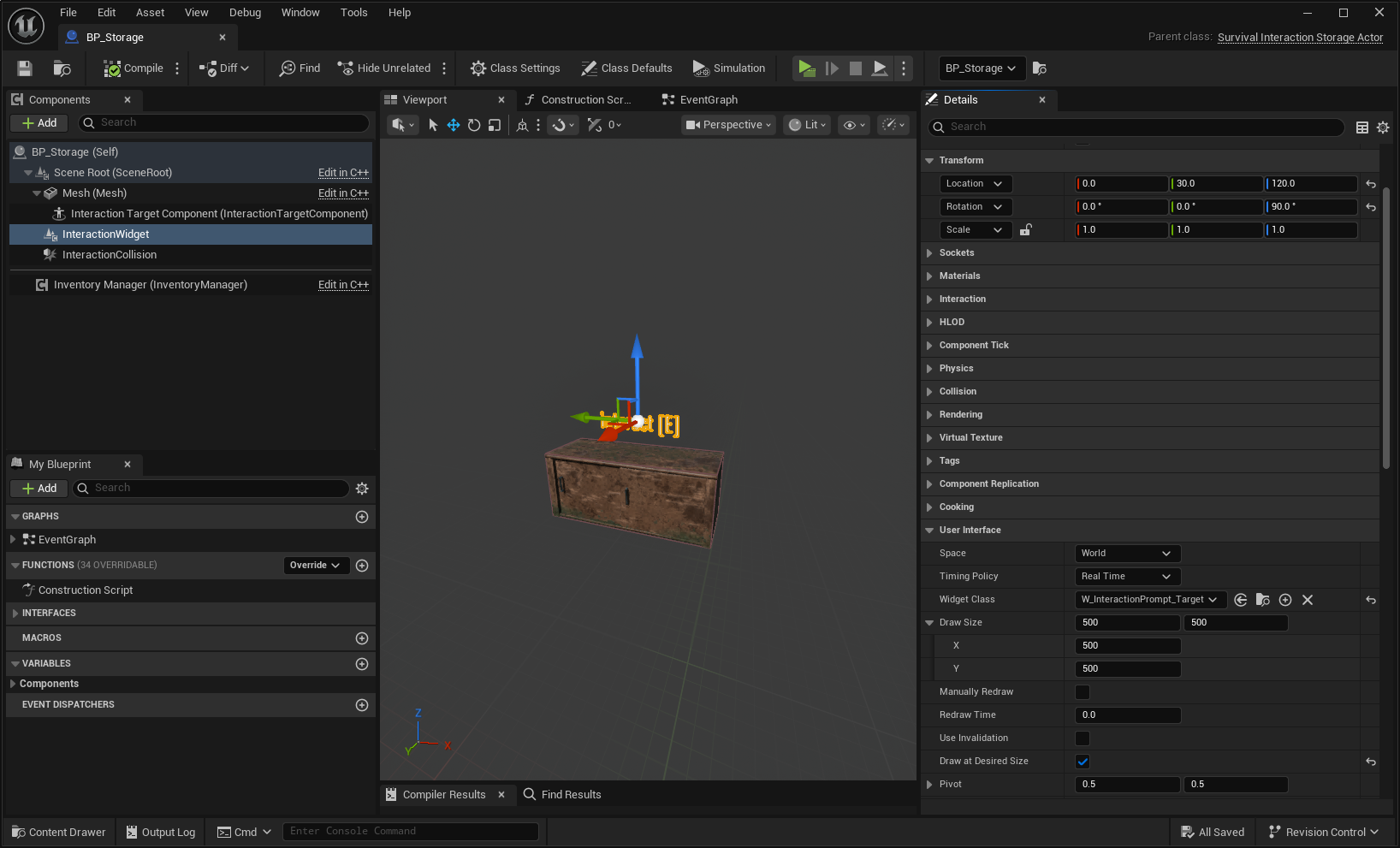
Actor prompts are placed on the Interaction Target actor using the UNinjaInteractionWidgetComponent.
Starting with the simplest possible widget, the steps below show how to build an interaction prompt that reacts to focus and interaction state using the Interaction Target ViewModel.
Creating a simple Interaction Prompt
Create a widget extending from your preferred base (e.g., User Widget or Common User Widget).
Design a minimal "Interact Prompt". This widget will be shown when focus is applied to the actor.
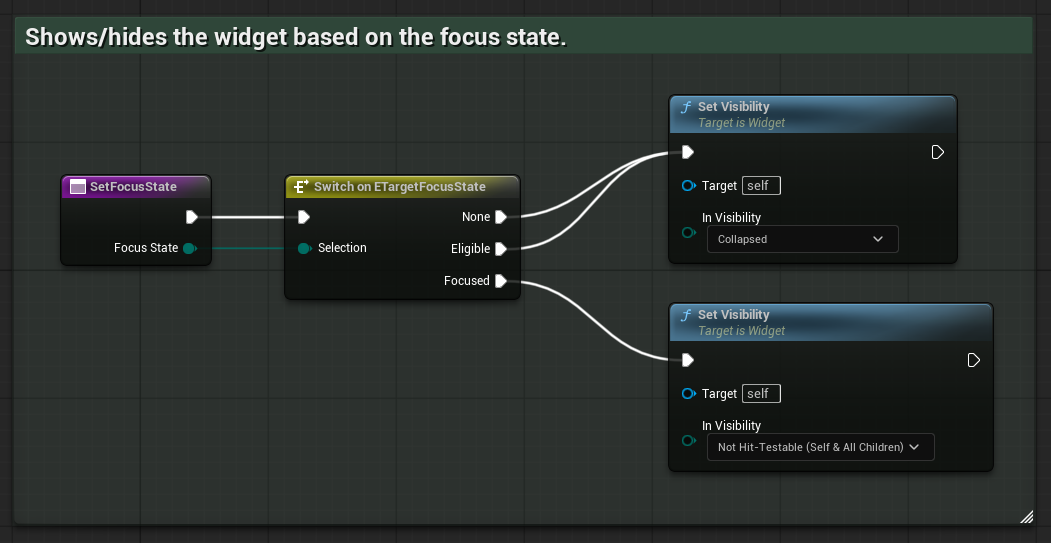
Implement
SetFocusState, receiving theTargetFocusStateenum. Set the widget's visibility based on the enum:None, Eligible →
CollapsedFocused →
Not Hit-Testable (Self & All Children)
Implement
SetInteractionState, receiving theTargetIInteractionStateenum. Set the widget’s visibility based on the enum:None, Commited, Finished, Cancelled →
CollapsedStarted →
Not Hit-Testable (Self & All Children)

Add the Interaction Target ViewModel to the widget. Set its Creation Type to Resolver and select the Interaction Resolver as the factory class.
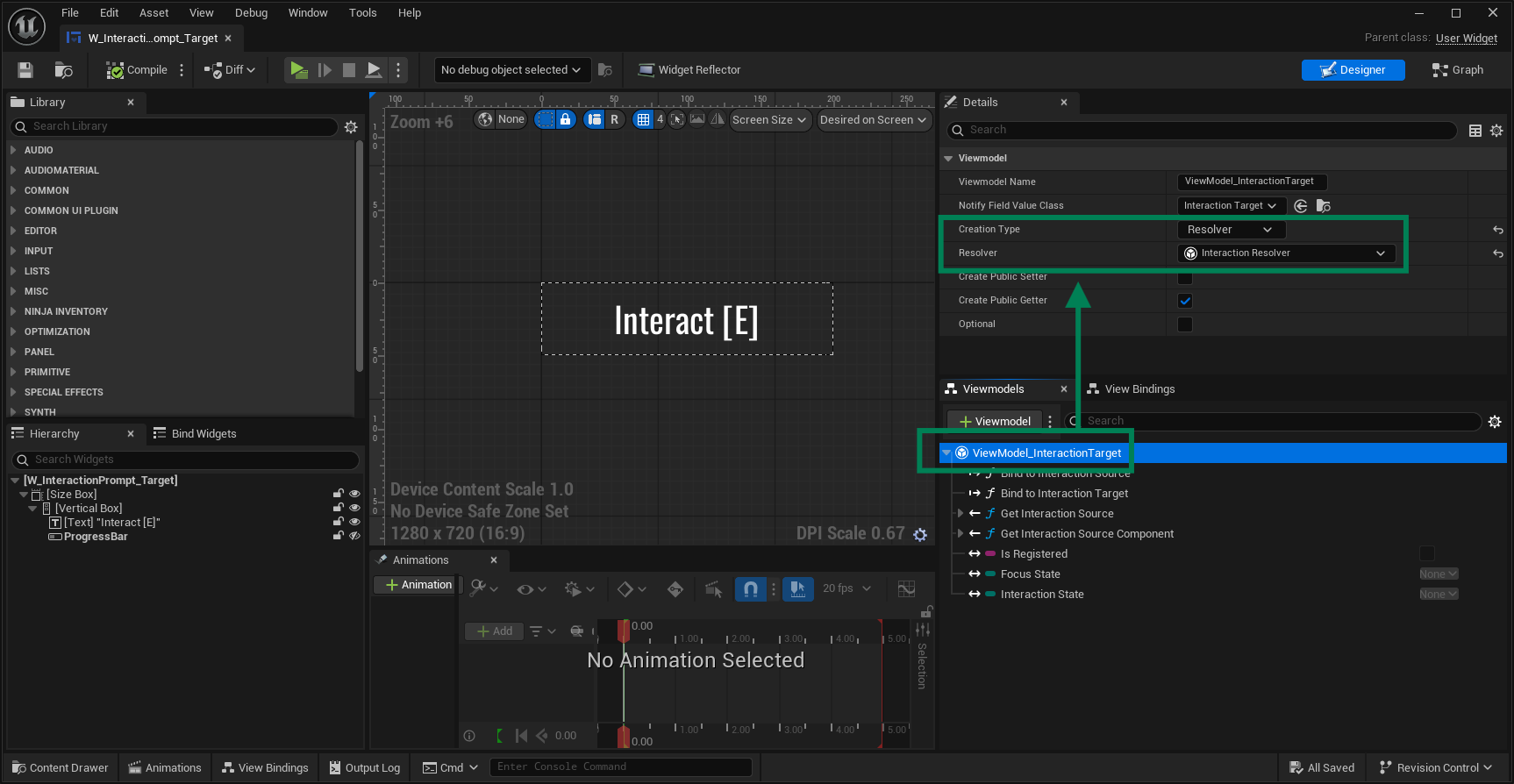
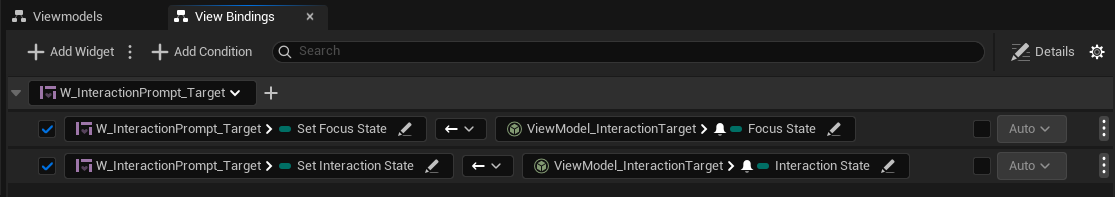
Bind the ViewModel's fields to your functions so the widget reacts to state changes:
Bind the focus state to
SetFocusStateBind the interaction state to
SetInteractionState
With the widget ready, assign it to your Interaction Target: